Psoriasis is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbations. Inflammation of the skin occurs in several stages: initial, progressive, stationary, regressive. This separation will aid in proper diagnosis and therapy.
Interesting to know
Psoriasis is a genetic disease. About 10% of the population has characteristic DNA disorders and only 2% of them show signs of a skin functioning disorder.
The following factors cause the appearance of pathology:
- strong emotional stress;
- lesions;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- unbalanced diet;
- infectious and other diseases;
- certain medications;
- endocrine diseases;
- predisposition to allergies;
Due to the incorrect response of the immune system, which reacts to the epidermal tissue as foreign elements, the first signs of the disease appear. Consider the stages of psoriasis, its symptoms, and treatment regimens.
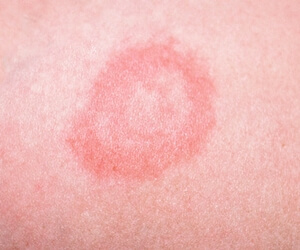
The early stage of psoriasis
The first sign isthe appearance of a pimple(papules). Rounded shape, reddish or pinkish color. In the lower extremities, due to slow blood flow, manifestations of a bluish tinge may appear. The papular formations are small, about the size of the head of a pin.
The initial stage is characterized bymany papulesthat have well-defined boundaries. Whitish scales also appear. They separate easily from the surface to the touch. Papules can merge into one, forming larger elements.
During initial remission, the lesions pale. The affected areas of the skin are partially discolored. In children, this stage of psoriasis is often mistaken for manifestations of allergies or diathesis. The rash may be accompanied by intense itching. Signs that can be used to diagnose psoriasis:
- when scraped, the surface of the plaque turns whitish, resembling a rubbed stearin drop, the scales peel off;
- if you continue to scrape the stain and remove the scales, a bright red surface will appear;
- when scraping, small drops of blood appear.
Progressive stage of psoriasis
During the progressive stage of psoriasis, the following symptoms appear:
- Papules turn red and continue to be covered with white scales. They peel off easily, underneath you can see a soft layer of reddened skin. When damaged, blood appears.
- With exacerbation, papular elements grow and merge. They are clearly different from healthy skin areas.
- Itching worse. But it happens during the transition of the process to the stationary phase. Obsessive, painful itching that interferes with sleep and daily activities. If you simply scratch the cover, lesions and new plaques will appear. The appearance of new plaques at the injury site is Koebner syndrome. The number of manifestations of itching gradually increases, covers the body, limbs and head.
- There are no scales on the edges of the plaques, they are hyperemic, indicating the continuation of the inflammatory process.
Consequences
Psoriasis can have a negative effect on the joints (psoriatic arthritis). Then there are severe pains in the joints, their deformation, if the process is left untreated.
Stationary stage of psoriasis
The main characteristic of the stationary stage of psoriasis is that new elements stop appearing. Positive changes come with the right treatment.
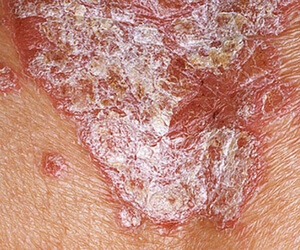
Clinical manifestations:
- the itch disappears;
- no lesions (Koebner's symptom disappears);
- can increase flaking.
All spots stop developing. If during the progressive stage the plaques had an edge without scales, then during the stationary stage the entire inflamed surface of the integument will shed and acquire a characteristic psoriatic appearance.
Scales are characteristic of the last stage of inflammation. At the beginning of the development of the pathology, the scales do not keep up with the progressive growth of the plates and cannot completely cover them. In half of the cases, apseudoatrophic corollaappears.
Pseudoatrophic corolla
It looks like a light border around the element, which has a structure reminiscent of rough tissue paper, which consists of a stratum corneum and does not exceed two millimeters in width.
Regressive stage of psoriasis
In the regressive stage of psoriasis, the psoriatic cycle ends. Featured Features:
- the exacerbation process stops, the inflammation disappears;
- plates dissolve gradually;
- peeling stops, elements of the rash are flattened;
- the rash turns pale pink, gradually fading;
- there may still be papules on the arms and elbows.
There are no scars or atrophies in the affected area. At the site of the rash, temporary hyperpigmentation or areas devoid of pigment may occur.
Remission occurs after complex therapy.The relief period is individual. Latent disease can last for several months or even years. Exacerbations occur most often in winter, with the exception of only some forms of psoriasis.
Treatment of psoriasis in different stages
The therapy of any form of psoriasis consists of general and local treatment, physiotherapy methods and diet adjustment. At an early stage of therapy, you need to:
- give up bad habits;
- strictly follow a therapeutic diet;
- use ointments containing vitamins A, D3, hormones;
- use systemic drugs and sedatives;
- undergo ultraviolet therapy.
If the plaques are on the head, the doctor prescribes shampoos based on tar, zinc, selenium sulfide.
All funds must be used as directed by a physician. Long-term use of medications (especially with tar) can irritate the skin. The funds must be changed every 7 days.
Early treatment of psoriasis
The effectiveness of early treatment interventions depends on when the patient sees the doctor and begins treatment.
Early therapy in most cases helps prevent the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Experts recommend using salicylic acid ointment. It is an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drug that has a beneficial effect on the affected skin areas. With the help of a keratolytic effect, the ointment will clean the plaque from the keratinized parts of the integument. Naphthalene ointment will help relieve itching.
Medications are generally prescribed:
- based on tar;
- based on solid oil;
- oil based.
Not long ago there were drops and oil for psoriasis. The tool can soothe the skin, hydrate it, prevent the skin from drying out, and relieve swellingThe preparation contains ubiquinone, beta-carotene, castor fat, propolis, pumpkin seed oil and other components, with the help of which the number of plaques decreases, they become less, and the skin is better hydrated. Its use is recommended in combination with other medications and after consulting with a specialist.
Treatment of psoriasis in a progressive stage
Therapy must be thorough and careful. The clinical picture is quite difficult, only specialists should trust the treatment. Intravenous and intramuscular administration of special drugs helps patients. Absorbents help remove toxins from the body.
Demonstrations remove salicylic acid ointment and emollient emulsions. They hydrate and reduce inflammation. During an exacerbation, drugs with tar in the composition or other irritating components should not be used.
Physiotherapy procedures (PUVA therapy, UV irradiation, paraffin applications) are best performed during the period of inflammation reduction. Corticosteroids and cytostatics are prescribed only when the processes are particularly complex.
Prescribe antihistamines (reduce the development of an allergic reaction), sedatives (painkillers), anti-inflammatories, keratolytics (emollients), diuretics (relieve swelling, eliminate toxins).
Treatment of stationary psoriasis
The patient needs a slight correction of the therapy. Usually prescribed shampoos with tar, emulsions with oil, calcipotriol. Systemic therapy is used when the disease affects large areas of the integument. Ultraviolet irradiation and the PUVA technique are widely used.
If there is no effect, some cytotoxic drugs are prescribed. In severe cases, the patient is prescribed an immunosuppressant, cytostatic.
Treatment of regressive psoriasis
The therapy in the last stage of psoriasis must be comprehensive, adjusted by a specialist. Therapy is gradually canceled, replaced by preventive measures. Treatment at all stages is carried out carefully, in no case should the rash be damaged.
Compliance with the strictest diet and lifestyle correction is of particular importance. Stress can be a powerful trigger, significantly aggravating the condition early in the disease.
In combination with drug therapy, hand rashes can be treated with sea salt baths or mixed baby cream with the powder of a series, lubricate the plates with this mixture.
Additional therapies
A patient with psoriasis has a lack of vitamins, which affect the regulation of metabolic processes, have a restorative, sedative and purifying effect on the blood.
The vitamin complex should contain B vitamins, ascorbic acid, vitamin A, folic acid and others. They are prescribed internally, intramuscularly, and also in droppers.
Dividing the pathology into different stages is a conditional measure that helps specialists to correctly identify one or another stage, facilitates diagnosis and treatment. It is impossible to completely get rid of psoriasis, but subject to all the rules of complex treatment, with systematic preventive measures, the disease can lie dormant for a long time and not maximally interfere with a person's life.























